Amphetamine Addiction: Symptoms, Side Effects & Treatment
What Are Amphetamines?
Amphetamine is a central nervous stimulant. Its use results in an increase in certain types of brain activity, resulting in a feeling of higher energy, focus, confidence, and in a dose-dependent manner, can elicit a rewarding euphoria. According to the Center for Substance Abuse Research, amphetamine was first synthesized in Germany in the late 1800s; however, its stimulant properties were not really discovered until about the 1930s, when it began to be used to treat nasal congestion.
As time went by, amphetamine began to be used to treat a variety of conditions, from alcohol hangovers to weight loss. It was also used to treat two conditions for which it is still known today: hyperactivity in young people (including attention deficit hyperactivity disorder) and narcolepsy, a condition in which people fall asleep suddenly. Occasionally, it is used to treat depression.
Types of Amphetamine
Multiple prescription medications contain amphetamine or its two active components, including:
Dexedrine is made from dextroamphetamine, which is one of the two active components of amphetamine, as described by the Food and Drug Administration; the other component is levoamphetamine. Dextroamphetamine is stronger than levoamphetamine, and it’s even stronger than amphetamine itself. Another well-known drug that is similar in structure to amphetamine but much stronger in effect is methamphetamine – an illicit stimulant that has a powerful euphoric effect and is highly addictive
and dangerous. In addition, the club drug known as ecstasy, Molly, or MDMA is a type of amphetamine that has a mind-altering effect.
How Are Amphetamines Abused?
Amphetamine is abused in a number of ways. Of course it is possible just to take the pills and experience a mild high that way. However, some people crush the pills and snort them, creating a faster, stronger high. One of the quickest ways to get high from amphetamine or methamphetamine is to dissolve the powder in water and inject it. This method gets the drug into the bloodstream and to the brain almost immediately, creating an intense high.
Students often abuse amphetamine through off-label use as a study aid. These individuals consider that the high energy and focus that result from using the drug can help them perform better on tests and in school. However, an article from TIME discusses a study that showed students who use amphetamines do not perform any better; in fact, they often perform worse. Nevertheless, the drug does make people feel like they can focus more and do better even if the opposite is true. More significantly, this level of abuse can lead to more severe, illicit use of the drug to get high.
The 2015 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) reports that about 4.8 million people in the US abused prescription amphetamine medications that year, equivalent to about 1.8 percent of the population that is 12 and older. The National Institute on Drug Abuse, on the other hand, reports that about 1.2 million people use methamphetamine; this is about 0.4 percent of the population.
Signs of Amphetamine Abuse
There are multiple ways of recognizing amphetamine abuse, including physical and mental symptoms and changes in behavior as described by Healthline:
- Increased heart rate and blood pressure
- Decreased appetite and weight loss
- Insomnia
- Digestive upset
- Mood swings
- Aggression
- Paranoia and anxiety
- Visual, auditory, or tactile hallucinations
- Inability to keep up with work, school, or home responsibilities
- Much of the person’s time spent seeking or using the drug
- Missing pills from a prescription
- Changes in groups of friends and difficulties with relationships
- Loss of interest in previous activities
If you or someone you love are struggling with addiction, get in contact with us by filling in our online insurance verification form below. Let us remove the confusion and difficulty of verifying your insurance coverage for treatment. We have years of experience in the addiction space and contracts with many of the big name insurance providers. By providing your name, contact information, and insurance provider, we can communicate directly with your insurance provider to find out if you are in-network with our facilities, the length of stay covered, and more without the hassle of having you contact them directly. All information is confidential and there is no obligation to enter treatment.
Amphetamine Addiction
As mentioned above, amphetamine is a highly addictive substance. Because of the way it acts on the body, this drug can cause changes in the way the brain behaves. In particular, amphetamine and related substances can significantly alter the brain’s
pleasure response, destroying pleasure receptors in the brain and decreasing the ability for the body to feel pleasure without using the drug.
The destructive properties of these drugs make people who abuse them feel depressed and even suicidal when they are not using the drug. As a result, cravings to keep using the drug can be very strong, making it difficult to stop use.
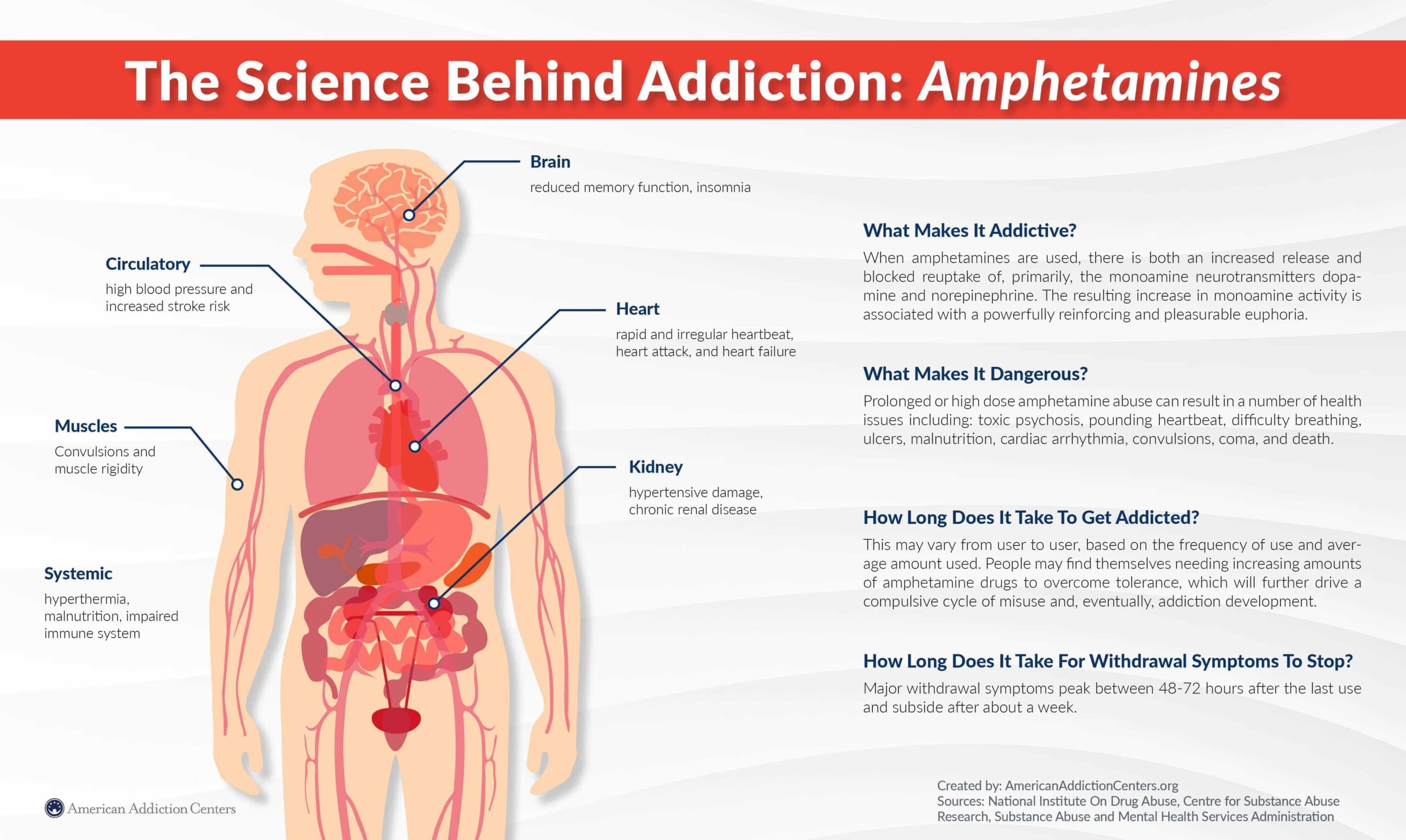
Amphetamine addiction can impact many different parts of the body including; the circulatory system, muscular system, systemic impacts, the kidneys, heart, and brain.
What Side Effects Are Associated With Amphetamines?
There are other short-term and long-term issues associated with amphetamine abuse that are related to the effects of these drugs on the body, as described by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, including:
- Increased heart rate and blood pressure
- High body temperature
- Loss of muscle control, muscle spasms, or tics
- Sleep disturbances
- Mood swings
- Low appetite
- Depression and fatigue when not using the drugs
In the long-term, these symptoms are often amplified. High blood pressure can cause damage to blood vessels and the heart, while elevated body temperature can cause damage to organs and tissues. Low appetite can lead to unhealthy eating habits and then to malnutrition, which can also damage the body and brain.
With methamphetamine, these problems can be even more exaggerated, leading to severe dental disease because of bad eating and lack of saliva, which leads to major infections and loss of teeth, as described by the American Dental Association. In addition, using meth can lead to skin damage due to hallucinations that something is “crawling” under the skin, leading people to pick at sores that then, due to damaged blood circulation, do not easily heal.
Treatment and Therapies for Amphetamine Abuse and Addiction
Treating amphetamine abuse and addiction can be challenging because of the changes in brain structure that occur with chronic use. The sometimes severe depression and loss of pleasure that occur when use of the drug is stopped can be a major obstacle to avoiding relapse. Nevertheless, therapies that help people understand and adjust their behaviors based on triggers of drug use can contribute to the individuals being able to get and stay on the path to recovery. These therapies include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
- Motivational Interviewing
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy
- Family counseling
- Addiction education
- Peer support or 12-Step group participation
By working with a reputable, research-based treatment program, individuals who have struggled with amphetamine abuse or addiction have a greater chance of moving forward in recovery and starting a future free from amphetamine abuse.

